About Skill India and Industry Partnership
The National Skill Development Mission, launched on 15th July 2015, aims to establish a comprehensive institutional framework to swiftly implement and expand skill development initiatives across India. Our Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, through the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), has undertaken several initiatives to foster partnerships with industries as part of the broader Skill India Mission. We offer a single-window facilitation system, providing a unique platform for industries to engage in various initiatives. Collaborating with a diverse array of stakeholders, including corporates, foundations, government entities, and community-based organizations, we design high-impact collaborative skill development projects.
-
 64
64
Partnerships
-
 INR 215.5 Cr
INR 215.5 Cr
CSR
Commitment -
 237
237
Districts
Covered -
 42
42
Aspirational
Districts Covered -
 105
105
Training Partners
Participation -
 71,438
71,438
Trained
(Short Term Training) -
 41,858
41,858
Placed
(Short Term Training)
- 532295 reads
- हिन्दी
How can you partner?
If you want to collaborate to add impetus to Skill India Mission, here’s a brief on models under which you can partner.
Industry Partnership Model
-
model 1 -Sponsorship of Candidates for Skill Development
- Contribute funds directly to the National Skill Development Fund (NSDF) or National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) to meet and fulfill CSR commitments under the Companies (Corporate Social Responsibility) Act, 2013.
- Sponsor candidates for skilling programs in priority areas/sectors (programs focused on livelihoods, persons with disabilities, minorities, special areas, etc.) in geographical area as suggested by company
- Operationalize Project through agreement amongst Company, NSDF and NSDC.
- Offer existing facilities and machinery for on-the-job training where available.
- Implement the project through NSDC Training Partners with project management support by NSDC at nominal cost (as per Common Norms Gazette Notification).
- Undertake Short Term Training of fresh candidates or Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) certification programs for employees (including contractual workers) for NSQF-alignment.
-
model 2 -Setting up Skill Centreof Excellence (CoE) /Multi Skill Center
- Setup/upgrade a skill development facility to be Centre of Excellence focused in sector/areas of strategic importance.
- The Centre of Excellence (CoE) to be of a state-of-the-art aspirational centre with highly advanced skill equipment with support from sector relevant industry, for promoting higher level of skilling in the country.
- Set up corporate owned multi-sectoral skill training centres/institutes.
- The centre may be operated directly by the Corporate or through NSDC affiliated Training Partner as per standards aligned to the NSQF.
- An agreement may be signed amongst the Corporate, NSDC and SSC to operationalize such projects.
- Combine with sponsorship of candidates’ trainings.
- Focus on Training of Trainer (ToT), Training of Assessor (ToA) programs, specialized programs focused on high skilled trades, etc.
- Establish collaboration with foreign partners to develop transnational standards through G2G/B2B partnerships with the support of NSDC.
- Co-brand centre/institute with Skill India.
- Utilize CSR funds and/or dovetail with Government schemes (like Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana) for sponsorship of candidates, where applicable.
-
model 3 -Support Trade-Specific Labs/Centers
- Corporate can setup/ donate labs to support skill development programs addressing industry need for skilled manpower at trade-level.
- Corporate, NSDC and the SSC can jointly identify training centres to upgrade/augment labs in such centres.
- Corporate can jointly monitor with NSDC to make certain such centres are delivering as per plan and on quality standards set forth.
- Ensure continuous engagement through technology and knowledge interventions, on-the-job training/apprenticeship programs for graduates, etc.
- Government schemes (like PMKVY) may be converged in such centres where focus is on underprivileged youth, to offset the cost of training and assessment.
-
model 4 -Right to use Land, Building, Machinery
- Provide right of usage to an appropriate facility to be used as a skill development centre.
- Support existing programs through basic setup costs and equipment donation to offset training programs that are cost intensive.
- Provision land usage for specific programs like Driver Training Centres, Construction-related trades, etc. with high employment potential.
- Operationalize through an NSDC affiliated Training Partner.
- Combine with sponsorship of candidates’ trainings.
-
model 5 -Skill Advisory
- NSDC to act as the Knowledge Partner and Industry as the Infrastructure Partner and/ or Implementation Partner to establish CoE or operationalize already existing centres.
- The combination of technical knowhow of Skills along with sector expertise assuring a highly aspirational centre with supreme training quality.
- The model necessitates active involvement of the Sector Skill Councils, ensuring alignment of sectoral requirements and expectations.
- The CoE model may be implemented in two ways as deemed feasible by the Funding Organization:
- The Funding Organization provide funds to NSDC for both Infrastructure or setting up the Training Centre/CoE and operationalizing the skill training project.
- The Funding Organization will set up the Infrastructure or the Training Centre/CoE, and will provide funds to NSDC for Skill Advisory where NSDC will facilitate operationalization the skill training project
- Participate in various activities of one or more relevant Sector Skill Councils in line with your business operations.
- Work directly with Sector Skill Councils to contribute to development of industry standards for skill development under the NSQF.
- Provide list of persons (including retirees) to be (master) trainers and assessors where feasible.
-
model6 -Supporting Apprenticeship through CSR
(Utilization of CSR funds for Apprenticeship training under ‘Skill training’ already covered under item no. (ii) of Schedule VII of the Companies Act.)
- CSR funds for Apprenticeship training to include expenditure on Basic Training and stipend payable to apprentices under Apprentices Act 1961.
- Expenditure on Apprenticeship training over & above of 2.5% i.e., minimum mandate as per Apprentices Act, can be utilized under CSR funding.
-
model 7 -Setup A Skill Development Organization /Business Unit
- Setup a Skill Development Organization either as a new business unit, independent trust/society or a newly incorporated special purpose vehicle with equity infusion from parent entity and/or promoters/trustees.
- Access funding from NSDC on subsidized terms
- Become a Non-Funding Training Partner where funding is not sought.
CSR for Skill India
COVID-19 pandemic is causing devastating impact in almost every country in the world. India, currently considered in the ‘acceleration phase’ of the virus, has number of positive cases increasing at an exponential rate. The Government’s decision to lockdown the country in order to diminish the spread of the virus has helped in contracting the spread. However, it is also turning into an impediment to underprivileged communities.
The Need
The marginalized, as a result of the lockdown, are out of jobs, forced to move back to their native places and most vulnerable to the pandemic in the absence of face masks, hand sanitizers and basic amenities including food and sanitation.
NSDC Inviting Contributions
NSDC in its endeavour to support the communities, aims to leverage its wide network of skilled workforce and implementation partners to take forward and implement the intentions through a set of models to achieve one inclusive goal – to reach out to underprivileged communities and strengthen their livelihoods.
NSDC urges you to contribute to this cause. The contributions will be utilized to support individuals who are currently unable to make ends meet, and communities that are most vulnerable to the virus due to the absence of basic necessities.
How the funds will be utilized?
-
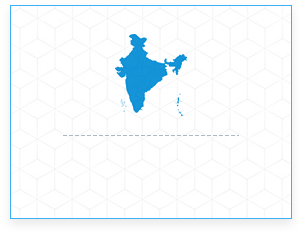
 Skilling, up-skilling and re-skilling of Paramedical Staff
Skilling, up-skilling and re-skilling of Paramedical Staff -

 Counselling modules in communities
Counselling modules in communities -

 eSkilling
eSkilling -

 Promote training in nano entrepreneurship to provide livelihood opportunities
Promote training in nano entrepreneurship to provide livelihood opportunities -

 Digital literacy, up-skilling and rehabilitation of Migrant Workers
Digital literacy, up-skilling and rehabilitation of Migrant Workers